Hyper Pigmentation
Introduction
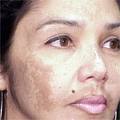
One of the main skin disorders that affect people in the Caribbean is hyperpigmentation (uneven skin tone and dark spots).
Many skin problems and medical conditions can lead to hyperpigmentation, including the aftermath of acne, razor bumps,melasma, chemical irritation, eczema, electrolysis, allergic reactions, abrasive scrubs, certain prescription medications such as oral contraceptives, pregnancy and hormones, obesity, thyroid disease, waxing, sunburn, insect bites, picking, wiping the eyes, tampering with the skin, trauma, tweezing, surgical procedures, and chemical peels.
Hormonal and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can be improved dramatically with light acid peels, conservative use of topical alpha hydroxy acids, and retinoids in formulations containing hydroquinone and other brighteners, sun avoidance and diligent use of non-comedogenic full-spectrum sunblock suited to your skin type.
Hyperpigmentation results from increased melanin which may occur in the epidermis, dermis or both
1> Normally the melanocytes are present in the basal layer of the epidermis and an increase in number or activity will cause epidermal hyperpigmentation
2> Formed melanin may be transferred to the dermis, or in some cases, dermal melanocytes are present. An increased activity or number of melanocytes in these instances will lead to dermal hyperpigmentation
3> Also a combination of the above may take place, resulting in mixed hyperpigmentation